Low angle normal faults with regional tectonic significance may be designated detachment faults.
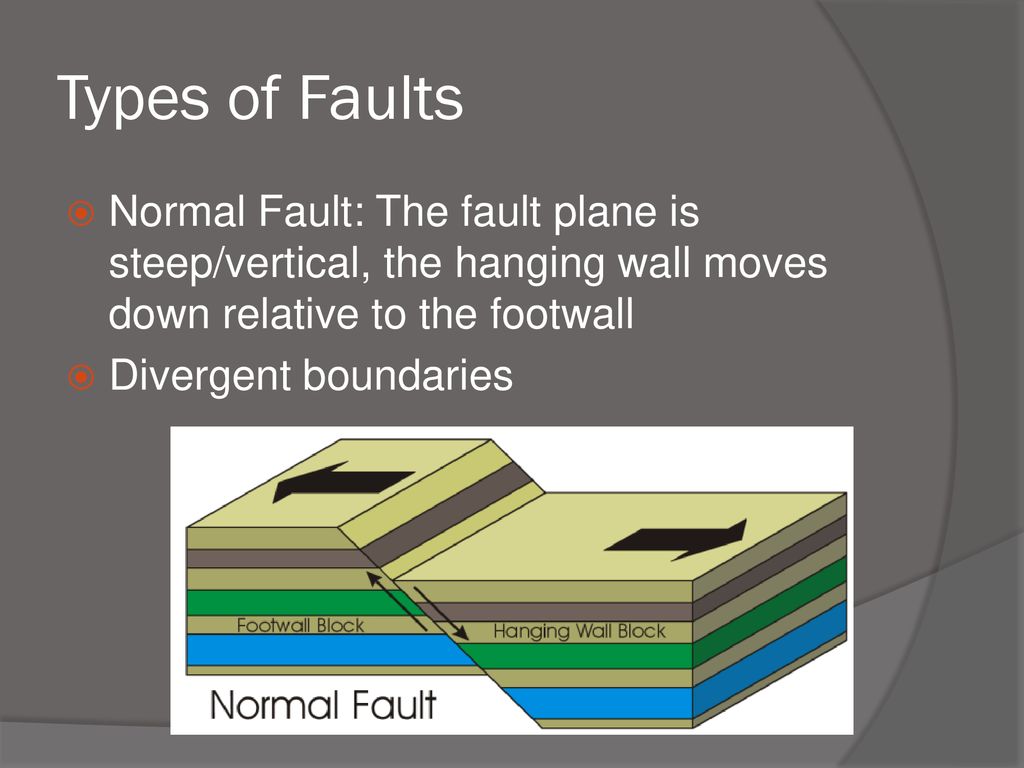
The hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
The hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
Normal dip slip faults are produced by vertical compression as earth s crust lengthens.
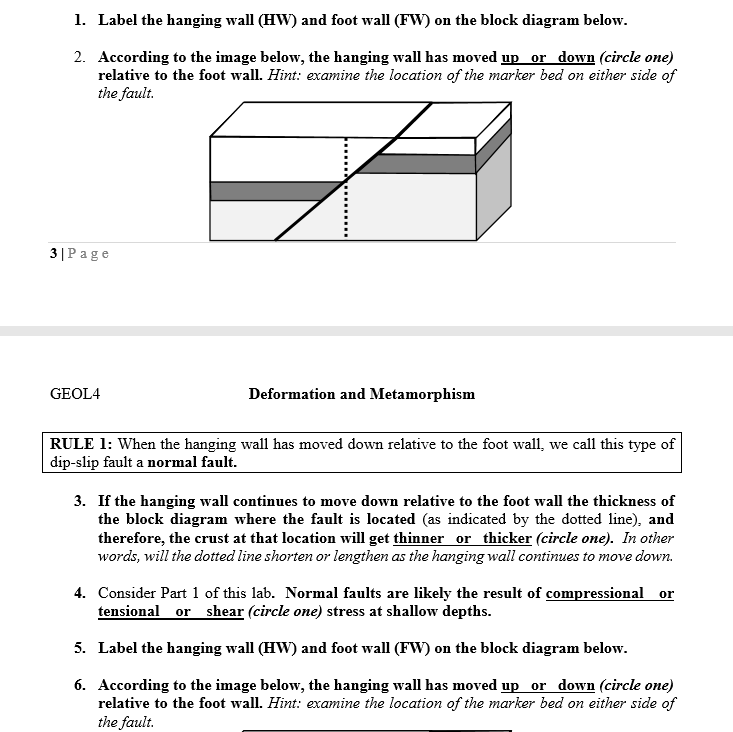
When the hanging wall moves down in relative to the footwall it is called a fault.
They bound many of the mountain ranges of the world and many of the rift valleys found along spreading margins.
Normal faults usually form where tectonic plate motions cause tension.
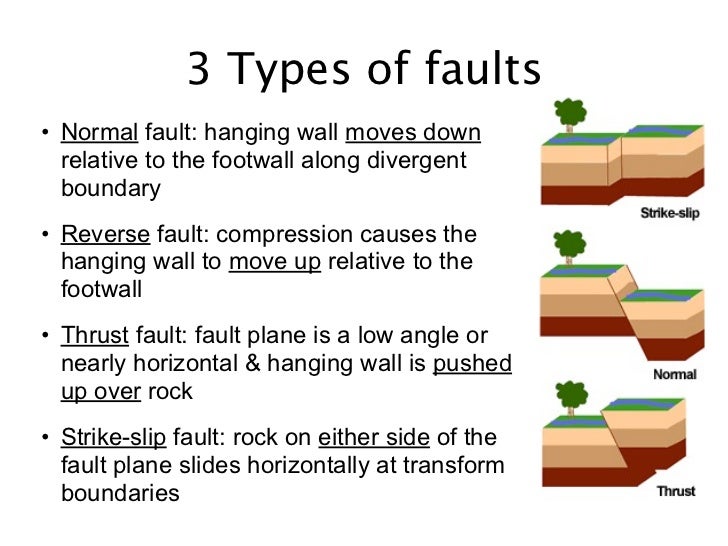
Another type of fault is the thrust fault where ground on one side of the fault moves up and over adjacent ground.
A normal fault occurs when the crust is extended.
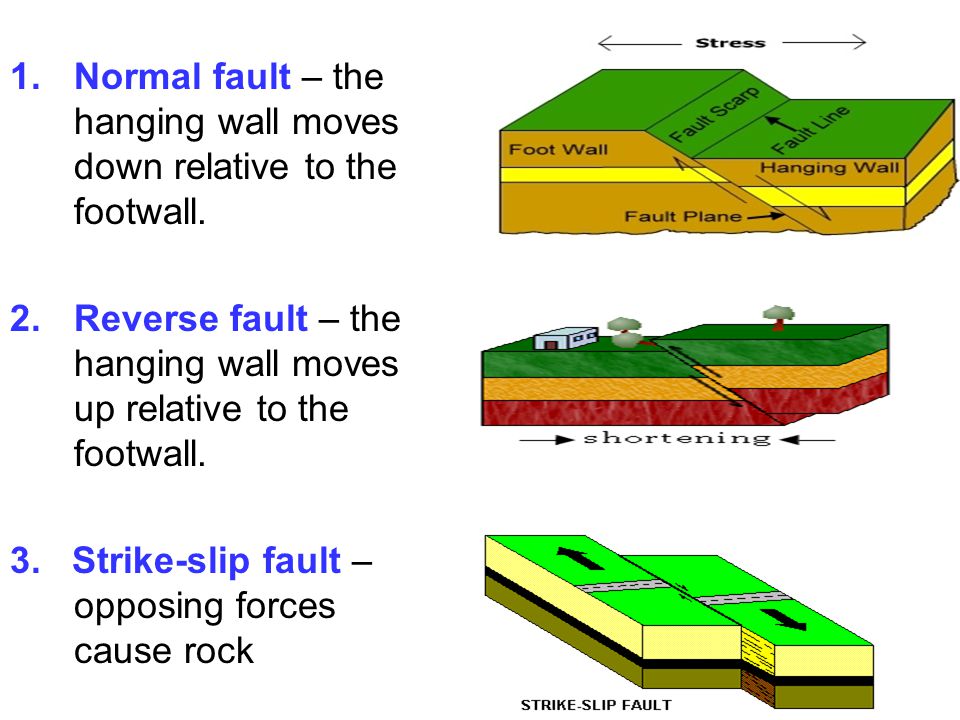
Along a normal fault the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall.
An upthrown block between two normal faults dipping away from each other is a horst.
When the hanging wall moves up in relative to the footwall it is called a fault.
In a normal fault the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
A downthrown block between two normal faults dipping towards each other is a graben.
These usually occur when tectonic forces cause tension that pulls rocks apart.
Tension is stress that pulls rocks apart.